



Low Access No Collaboration No Accountability

Too complicated Not flexible Not Customisable
If your company doesn't have their systems in order it could cost hundreds of thousands of dollars in fines! 💸
Prosecution Legal fees Pointless paperwork
Get your H&S in order to save lives AND your bottom-line.

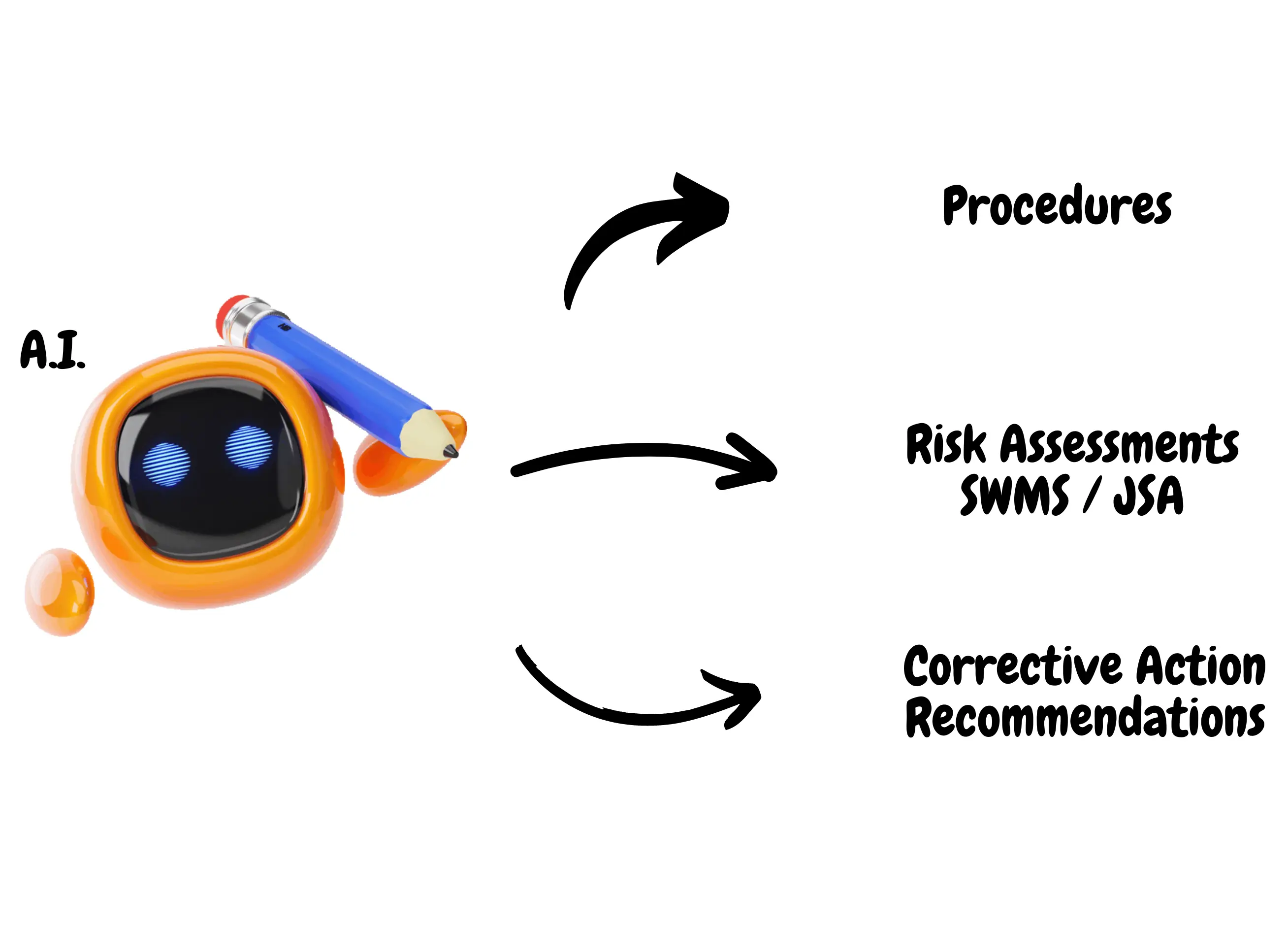
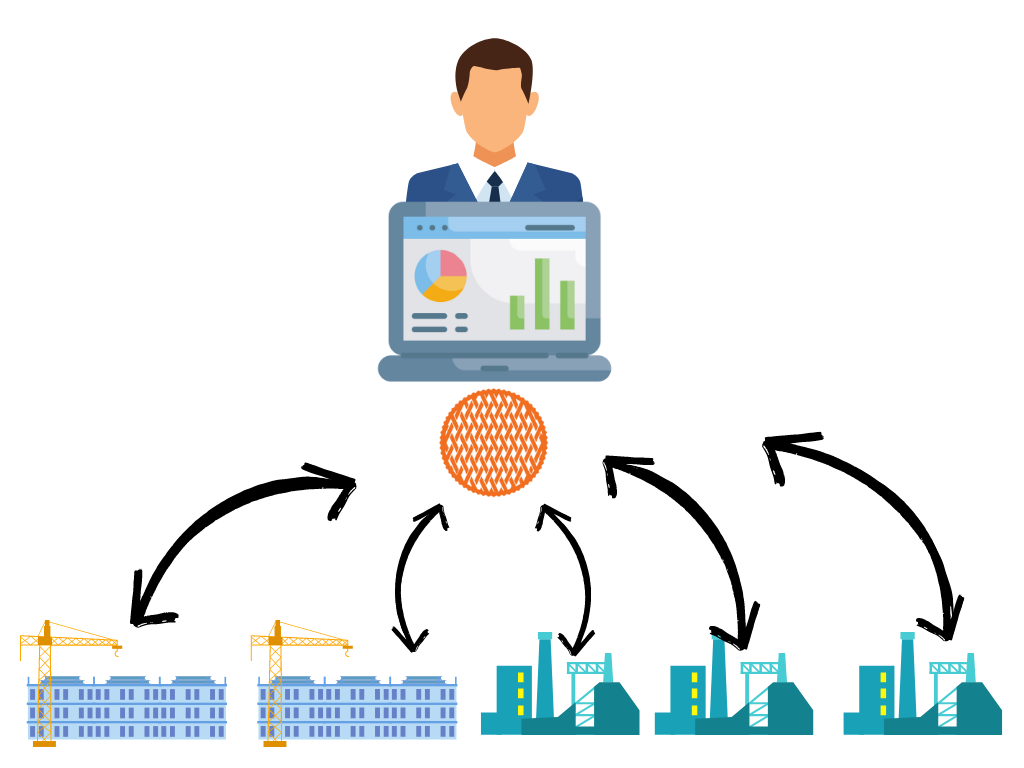
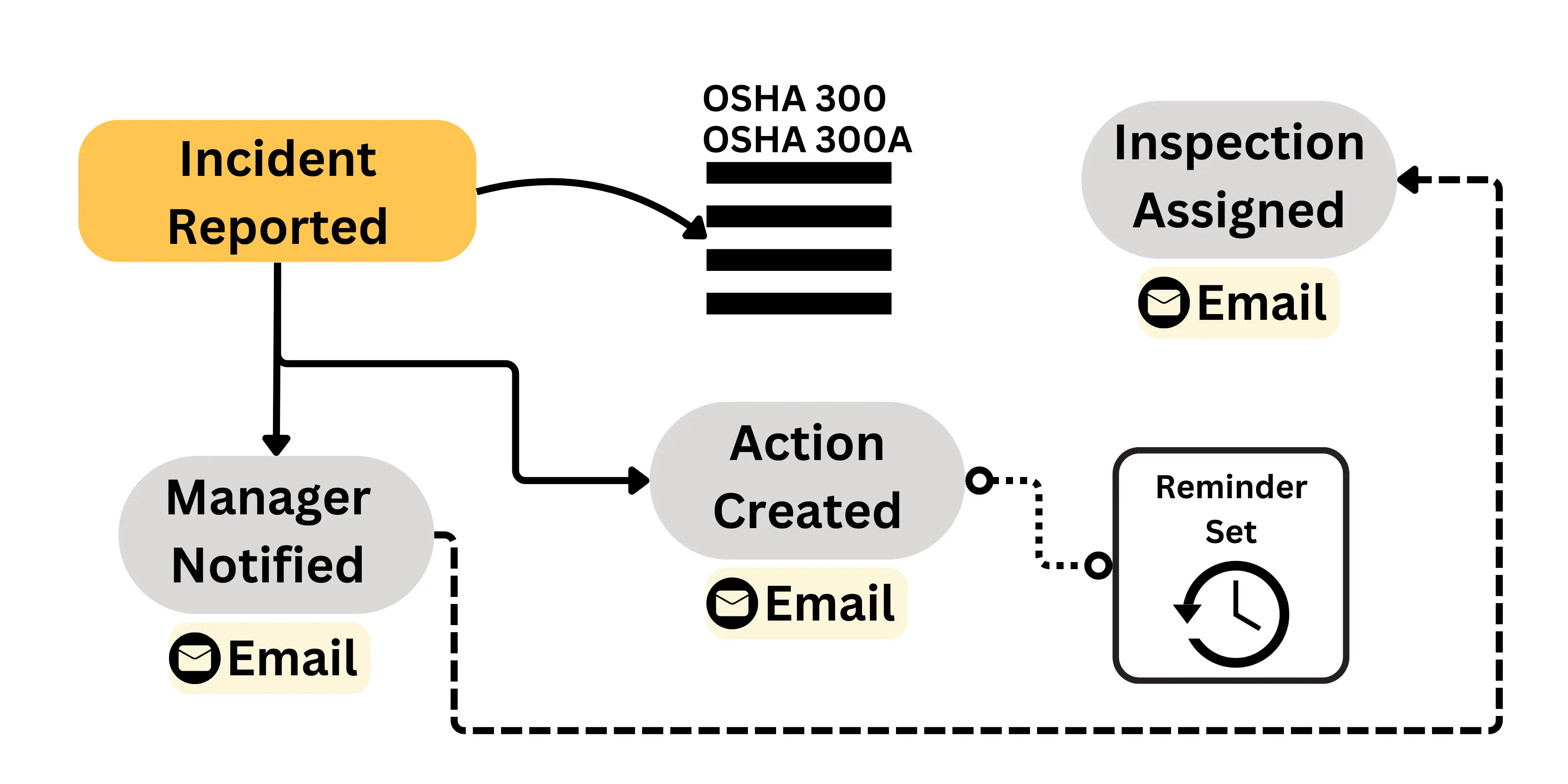




Monthly contracts, Cancel at any time
Book a FREE demo with our team
We'll do the setup for you
Book a DemoIn this free consultation we'll show you:
